Discuss, Definition and Terms. 5pts each 1.Bits and Bytes.- A BIT, is a BINARY DIGIT. A bit can be a zero or a 1 These collections of bits can represent binary numbers.
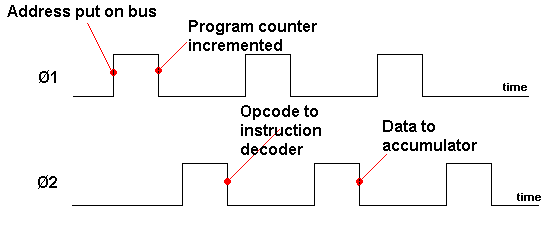
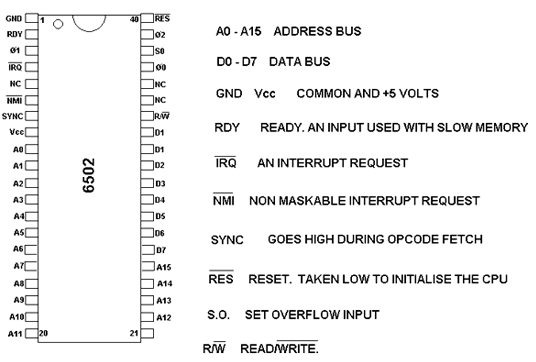
2. Microprocessor System Diagram The CPU can put a binary number on the address bus, to select an individual register in the ROM or ram or the I/O.
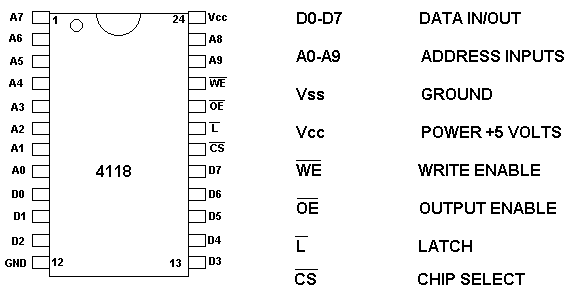
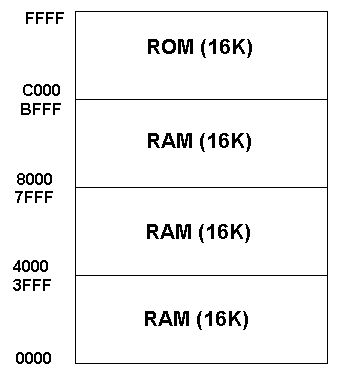
4. ROM Memory chips are simply a collection of registers , each with its own address.Data, in the form of 0's and 1's, is stored in the registers.ROM chips can be read from, but not written to.They are non volatile, which means that they retain their contents after power is removed.Most ROMs are programmed during manufacture of the chips.Others, PROGRAMABLE ROMS, PROMS, can have their contents programmed in after manufacture.The 2716 ROM shown above is an EPROM. 5. Instructions and Programs Instructions are represented by binary numbers called operational codes, or OPCODES.
Different CPU's have different instructions. ex .ADD add to the contents of the accumulator.
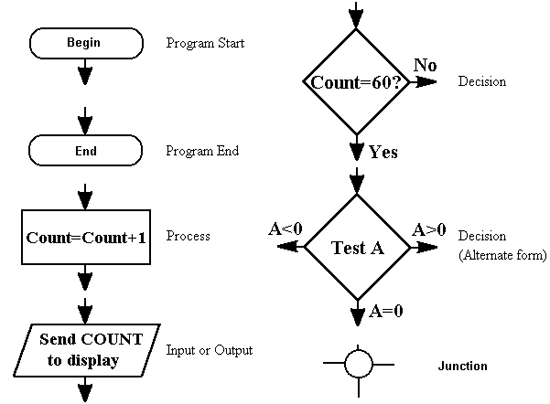
A program is a list of instructions, usually written using mnemonics. Here is the sequence of events for writing programs. Define the problem.Produce an algorithm (a list of instructions, written in everyday language). Produce a flow chart. Write the program using mnemonics. Assemble into hex opcodes. (an assembler is a program which does this). Test by running the program. DEBUG IT !! 6.Flow Chart Symbols When planning software, one of the stages is to produce a flow chart.The shape of the box indicates its function.Further data is given as text inside the box. 7. Interrupts Interrupts Tutorial
Flo
w Chart Symbols Tutorial
.
Arithmetic / Logic Unit Tutorial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Friday, September 17, 2010
TESTI
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)




No comments:
Post a Comment